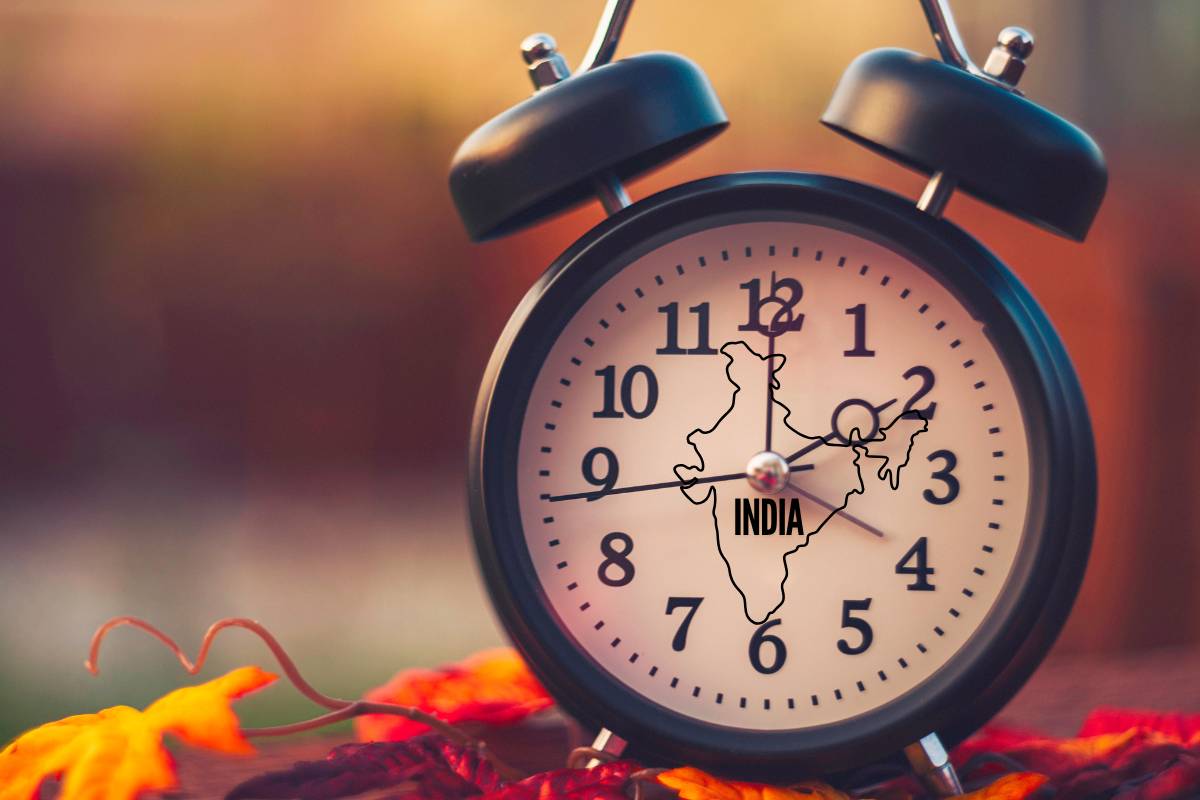
India is a land of diverse cultures, ancient traditions, as well as rapid modernization. This land represents one unique time zone, the IST. Many countries stretch more than one time zone; on the other hand, India manages with only one time zone, making its vast expanse homogenous under the same standard time. The article describes and elaborates on the specifics of IST, its significance, and its impact on all kinds of life and commerce.
Table of Contents
ToggleIndia Standard Time (IST) is the time that is across the country and is at the same value as UTC +5:30.This therefore means that IST is UTC plus 5 hours 30 minutes. Now it is pretty evident that India opted for a specific time zone with considerations to its history and geographic location.
This is Friday, 29 November 202,4 local time 11:00 PM in India. For all major cities like New Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, and Kolkata, it is now at the same time. In this way, IST harmonization makes scheduling and conducting businesses and traveling throughout the nation easier.
India has followed a single time zone since the British colonial period. Before standardization, local mean time was followed in different regions, which caused confusion and inefficiency. In 1906, IST was founded, based on the 82.5° East longitude near Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh, to establish a uniform time standard for the whole country.
IST has a lot of impacts on everyday life in India as follows: Work and Business: Businesses can operate continuously in all states with only one time zone. In cases of business operations such as telecommunications and transport industries that need to be uniformly aligned, it is useful for the business to thrive without disruptions. Education: As there is one time zone, school schedules and exams are uniform from coast to coast. Travel and Transport: Trains, flights, and bus timetables are also standardized, thus avoiding much confusion over the time zone, and a traveler can prepare better for travel.
The +5:30 hour offset that India has concerning UTC is a challenge globally, but it is also an opportunity:
International Business: Many Indian companies operate with business partners in different time zones. Thus, it is very important to know about IST while scheduling meetings and coordinating projects. For instance, while it is 9:00 AM EST in New York, it is already 7:30 PM in India.
Outsourcing and IT Services: Most global companies outsource their IT and customer service functions to India. The time difference helps the Indian teams work at times when the other hemisphere is asleep.
Cultural and Social Connection: The internet and social media have made it easier to interconnect the world. Knowing IST enhances people’s ability to communicate globally with their friends, families, and colleagues in India.
Though IST offers many benefits, there are also certain disadvantages: Geographic Extremes: The eastern and western parts of India are quite different in daylight hours.
For example, the sun rises and sets much earlier in the eastern state of Arunachal Pradesh compared to the western state of Gujarat. India can be of multiple time zones to synchronize more with actual daylight hours. This, though administratively and logistically not possible, has not found any takers.
Experts and government bodies have suggested a dual time zone system for India. This aims to reduce the daylight hour differences between the east and west. States such as Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Manipur see sunrise and sunset much earlier than Rajasthan or Gujarat. This mismatch causes a loss of daylight hours in the East. It also leads to higher electricity use in the evening.
The Indian government believes that having one time zone helps with efficiency and national unity. Some groups support a new time zone called “Bagaan Time.” These include the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the National Institute of Advanced Studies (NIAS). This time zone is used informally in some northeastern states.
The talk about a second official time zone is still ongoing. This debate shows the need to balance geographical differences with the simplicity of India’s timekeeping rules.
To convert IST to other time zones, follow these guidelines:
EST (Eastern Standard Time): IST + 10:30 hours (IST is 10 hours, 30 minutes ahead)
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time): IST – 5:30 hours (IST is 5 hours, 30 minutes ahead)
CET (Central European Time): IST – 4:30 hours (IST is 4 hours, 30 minutes ahead)
These conversions are key for travelers, businesses, or anyone coordinating activities across time zones.
IST impacts over a billion people. It affects business operations, school schedules, and social connections. So, despite the challenges, it still forms the backbone of India’s identity. It also serves as the foundation for a united and efficient society. Knowing IST is important for global business operators, travelers, and time zone enthusiasts. It helps you understand its impact worldwide.